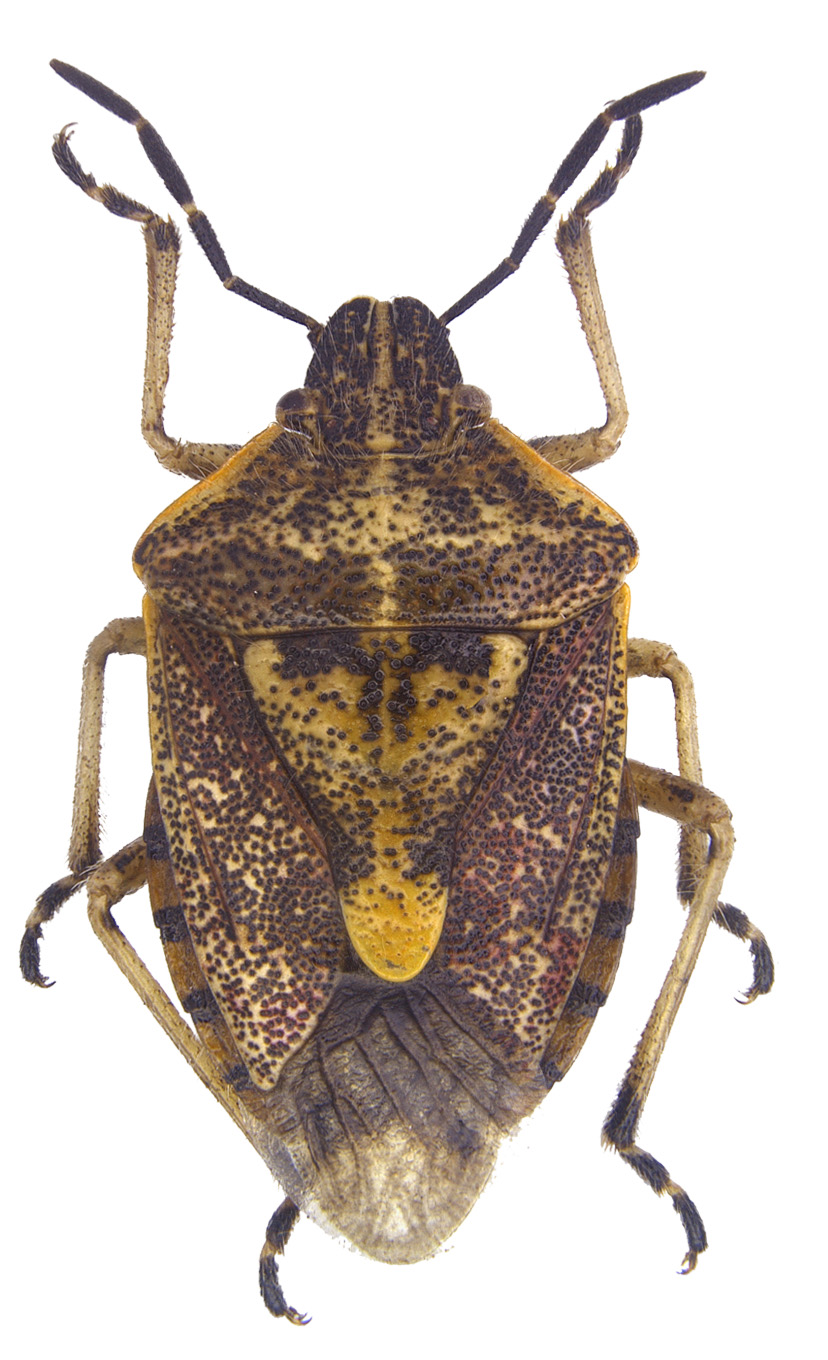
Dolycoris indicus Stal, 1876
Synonyms
Carpocoris (Dolycoris) Mulsant & Rey, 1866
Carpocoris Kolenati, 1846
Taxonomic position
Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae: Pentatominae
Diagnosis
- Head with apex truncate
- Mandibular plates slightly longer than clypeus. not meeting in front of clypeus
- Antero lateral margins of pronotum obliquely straight, smooth; humeri rounded
- Peritreme spout-shaped, not reaching middle of metapleuron
- Legs with femora unarmed, tibiae dorsally with indistinct narrow, longitudinal groove, tibiae not dilated.
- Body with small pubescence
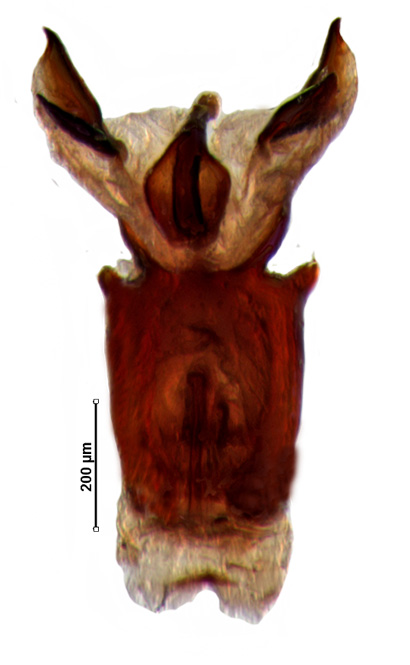
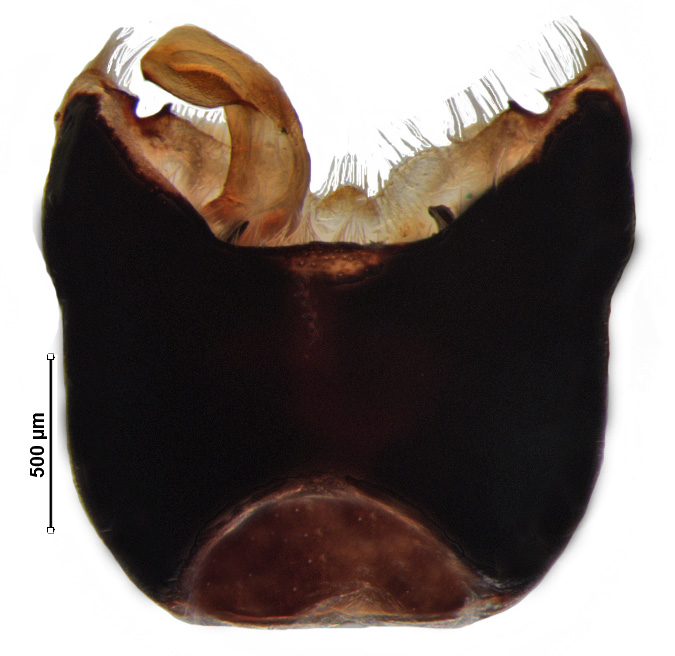
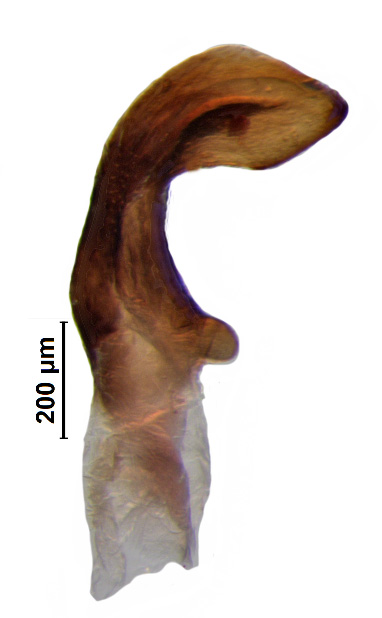
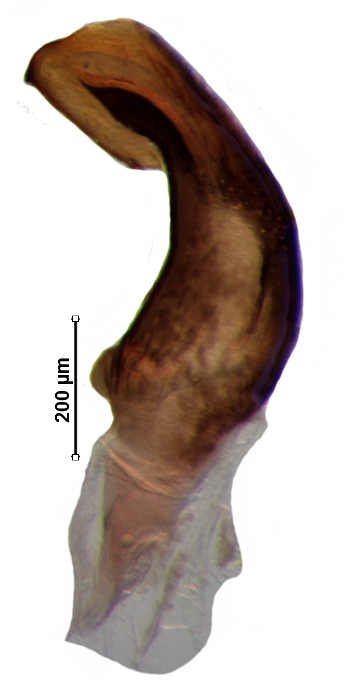
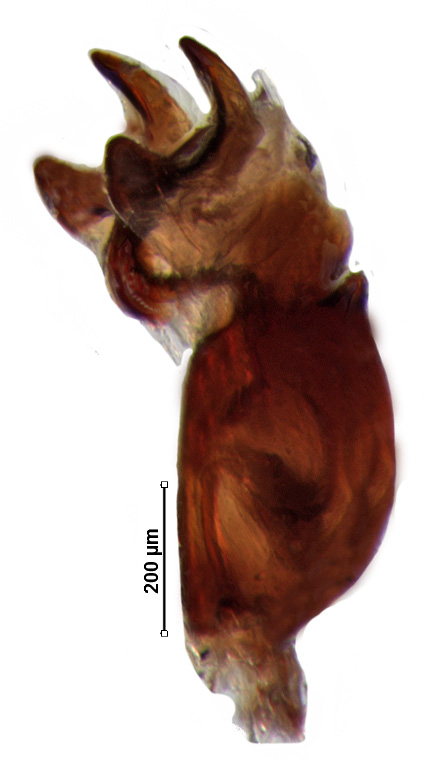
Male genitalia
Genital capsule with ventral rim widely excavated and concave; caudal lobes bearing small tuft of hairs; dorsal rim deeply concave with small median emargination; paramere nearly C-shaped with moderately expanded crown; phallus with phallotheca constricted distally; one pair of short finger-like thecal process; one pair conjunctival process; processes of aedeagus fused with aedeagus throughout its length; aedeagus nearly sickle-shaped.
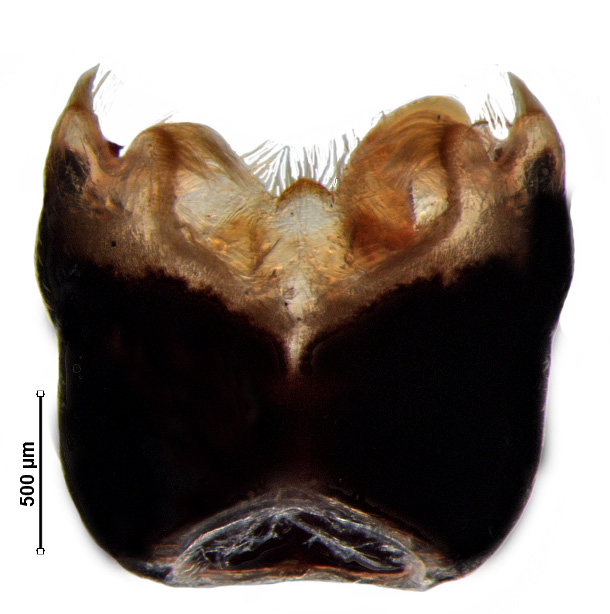
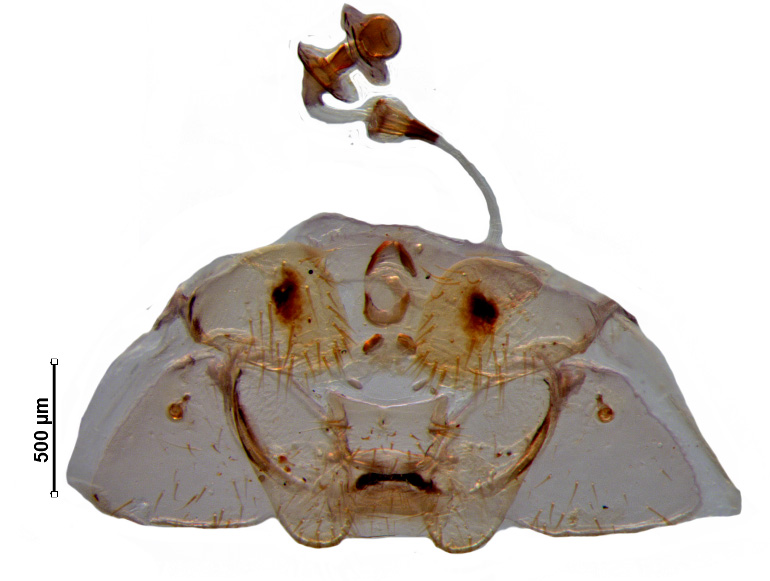
Female genitalia
Valvifers VIII roughly elongate oval; valvifers IX roughly trapezoidal; laterotergite IX oblique, elongate oval with rounded apex; laterotergite VIII roughly triangular with smooth caudal margin; spermathecal dilation reduced to small, spherical bulb-like structure; apical receptacle orbicular, without any finger-like structure.
Biology
Eggs laid in 5-6 batches, each consisting 10-14eggs arranged in rows, glued vertically to the undersurface of the leaves. Freshly laid eggs are creamy white in colour, barrel shaped and reticulately sculptured with T-shaped egg buster. The incubation period varies from 2-3 days (Ahmad & Akhtar, 2015).
Host plants
Lantana (Chatterjee, 1934); Cruciferous vegetables (Ahmad and Akthar, 2015); Trifolium alexandrinum Linn., Phaseolus mungo, Brassica sp. (Azim, 2011).
Distribution
Assam (Kirkaldy, 1909); Bihar (Fletcher, 1920); Jammu and Kashmir (Azim, 2011); Karnataka (Salini, 2006); Maharashtra (Distant, 1902); Nagaland: (Distant, 1902); Odisha: (Fletcher, 1920); Punjab: Jallandhar (Fletcher, 1920); Tamil Nadu (Chatterjee, 1934); Uttar Pradesh (Azim, 2011); West Bengal (Atkinson, 1887); Deccan Plateau (Atkinson, 1887); Throughout India (Chatterjee, 1934).
India (Distant, 1902); Pakistan, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Myanmar (Rider et al., 2002); China, Oriental region (Aukema & Rieger, 2006).
Selected References
Ahmad, T & Akhtar, N. (2015) Taxonomy and biological observations on two pentatomid pests Dolycoris indicus Stal and Eurydema pulchrum Westwood attacking agricultural crops in Kashmir Valley. Int. J. Entomol. Res., 03 (02), 55-59.
Azim, M. N. (2011). Taxonomic survey of stink bugs (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) of India. Halteres, 3, 1-10.
Chatterjee, N. C. (1934) Entomological investigations on the spike disease of sandal (24). Pentatomidae (Hemipt.). Ind. For. Rec., 20, 1-31.
Distant W.L. (1902). The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Vol. 2. London, xvii + 1-242.