Scientific name
Hippodamia variegata (Goeze) (=Adonia variegata (Goeze))
Common name
Adonis ladybird, Variegated ladybird
Taxonomic position
Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Coccinellinae: Coccinellini
Diagnosis
Length 3.0-5.5 mm, width 2.4-3.0 mm. Form narrow, elongate oblong-oval, and weakly convex. Head yellow with a black transverse marking in posterior half, reaching nearly up to middle of eyes. Pronotum black with white anterolateral margins and a pair of median eye spots/markings, sometimes fused together. Scutellum black. Ground colour of elytra orange yellow, brick red or bright red, with whitish/creamy yellow areas adjacent to scutellum and a maximum of thirteen black spots-one postscutellar spot and six on disk of each elytron; elytral pattern highly variable, only subscutellar spot always present, other spots variously confluent or obsolete. Ventral side more or less completely black, except
pronotal hypomera, elytral epipleura and parts of legs yellowish brown. Antenna (Fig. 1) 11-segmented, terminal segment distinctly transverse. Terminal segment of maxillary palpi (Fig. 2) elongate, securiform. Postcoxal line (Fig. 3) complete, very shallowly arched. Male genitalia (Figs. 5-6) and female spermatheca (Fig. 4) as illustrated. 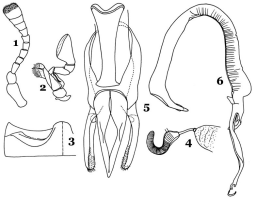 Figs. 1-6. Hippodamia variegata (Goeze): 1. Antenna; 2 .Maxilla; 3. Postcoxal line on abdominal ventrite 1; 4. Female spermatheca; 5-6. Male genitalia: 5. Tegmen, ventral view; 6. Sipho Figs. 1-6. Hippodamia variegata (Goeze): 1. Antenna; 2 .Maxilla; 3. Postcoxal line on abdominal ventrite 1; 4. Female spermatheca; 5-6. Male genitalia: 5. Tegmen, ventral view; 6. SiphoImages

 Adult Adult
Distribution
India: Arunachal Pradesh; Delhi; Gujarat; Himachal Pradesh; Jammu & Kashmir;
Karnataka; Maharashtra; Punjab; Uttar Pradesh; West Bengal. Nepal. Bhutan. Pakistan. Myanmar. China. Europe. North Africa. North America.
A Palaearctic species, also widely distributed in the Afrotropical and Oriental regions. Commonly distributed in the plains of north India and up to
14000-15000 feet in the Himalayas. This species seems to be expanding its geographical range into western and peninsular, going by the increasing number of specimens collected from Gujarat, Maharashtra and, recently, Karnataka (Belgaum and Dharwad districts).
Prey / Associated habitat
HEMIPTERA: Aphidoidea: Adelges spp., Aphis craccivora Koch, Aphis fabae Scopoli, Aphis gossypii Glover, Aphis malvae (Koch), Aphis spiraecola Patch,
A. umbrella (Boerner), Brachycaudus cardui (Linnaeus), Brachycaudus helichrysi (Kaltenbach), Brachycaudus pruni (Koch), Brachyunguis harmali Das, Brevicoryne brassicae (Linnaeus), Dreyfusia (as Adelges) knucheli (Schneider-Orelli & Schneider) (as Chermes himalayensis Stebbing), Diuraphis noxia (Mordvilko), Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann), Hyalopterus atriplicis (Linnaeus), Hyalopterus pruni (Geoffroy) (as H. arundinis auctt.), Hayhurstia atriplicis (Linnaeus), Hyperomyzus carduellinus (Theobald), Liosomaphis himalayensis Basu, Lipaphis pseudobrassicae (Kaltenbach) (as L.
erysimi (Kaltenbach)), Macrosiphum rosae (Linnaeus), Myzus ornatus Laing, Myzus persicae (Sulzer), Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) (as Macrosiphum granarium (Kirby)), Sitobion graminis Takahashi, Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi), Toxoptera aurantii (Boyer
de Fonscolombe), Uroleucon sonchi (Linnaeus). Margarodidae: Drosicha stebbingi Green. LEPIDOPTERA: Noctuidae: Helicoverpa armigera (Huebner). ACARI: Tetranychidae: Tetranychus urticae Koch (as T. telarius Linnaeus). Collected in association with aphids on wheat, maize, pearl millet, cabbage, cauliflower, lucerne, safflower, carrot, bhendi, mustard, berseem,
apple, linseed, bittergourd, etc. and adelgids on silver fir pine, and other conifers.
Seasonal occurrence
Common during February-July; collected during February and September-December in north and northwestern regions (label data); January (Karnataka).
Natural enemies
Dinocampus coccinellae (Schrank); Homalotylus flaminius (Dalman), Oomyzus scaposus (Thomson), Hyperteles sp. and Parachrysocharis sp.; Verticillium
lecanii (Zimmerman) Viegas.
References
- Bielawski, R. 1972. Die Marienkafer (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) aus Nepal.
Fragmenta Faunistica, 18: 283-312.
- Booth, R.G., Cox, M.L. & Madge, R.B. 1990. IIE Guides to Insects of Importance to Man. 3. Coleoptera. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, 384 p.
- Kapur, A.P. 1942. Bionomics of some Coccinellidae predaceous on aphids and coccids in north India. Indian Journal of Entomology, 4: 49-66.
- Kapur, A.P. 1957. Variation in the colour pattern of certain ladybird beetles from high altitudes in the Himalayas. Bulletin of the National Institute of Sciences of India, 9: 269-273.
- Sharma, P.K. & Verma, A.K. 1993. Studies on the coccinellid predators of the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae in Himachal Pradesh. Journal of Biological Control, 7(2):
15-19.
- Stebbing, E.P. 1903. Coleoptera 2. Notes upon the known predaceous Coccinellidae of the Indian region, Part I. Indian Museum Notes, VI(1): 47-62.
|