Scientific name
Scymnus (Pullus) coccivora Ramakrishna Ayyar, 1925: 491. (=Scymnus coccivora Ayyar, Pullus coccidivora, Scymnus (Pullus) elegans Sicard, Scymnus (Pullus) elegans var. clathratus Sicard, 1929)
Taxonomic position
Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Scymninae: Scymnini
Diagnosis
Length 1.70-1.90 mm, width 1.20-1.30 mm. Form elongate oval, moderately convex. Ground colour pale golden yellow to yellowish brown, with dark purplish brown markings on elytra. Elytra with an hour glass-shaped longitudinal marking in basal half, which sometimes appears as two distinct markings; two small circular spots present in posterior half; elytral pattern variable, sometimes with only
posterior spots present or uniformly yellowish brown, completely devoid of markings. Antenna (Fig. 1) 11-segmented. Prosternal intercoxal process (Fig. 3) with a pair of carinae, broader towards posterior. Postcoxal line (Fig. 2) complete and semicircular, area adjacent to postcoxal line smooth. Male genitalia (Figs. 4-6) as illustrated. Larva with dorsal surface covered with white waxy filaments.
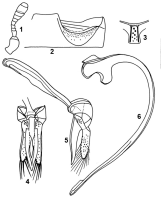 Fig.1-6. Scymnus coccivora Ayyar: 1. Antenna; 2. Postcoxal line; 3. Prosternal intercoxal process; 4-6. Male genitalia: 4. Tegmen, ventral view; 5. Tegmen, lateral view; 6. Sipho Fig.1-6. Scymnus coccivora Ayyar: 1. Antenna; 2. Postcoxal line; 3. Prosternal intercoxal process; 4-6. Male genitalia: 4. Tegmen, ventral view; 5. Tegmen, lateral view; 6. SiphoImages





 Adult Adult

 Adult without elytral spots Adult without elytral spots
 Larva feeding on mealybugs Larva feeding on mealybugs
Distribution
Widely distributed throughout India (Andhra Pradesh; Karnataka; Kerala; Madhya Pradesh;
Tamil Nadu; Uttar Pradesh). Pakistan. Sri Lanka. Thailand. Malaysia. Papua New Guinea. Introduced into the Caribbeans (Trinidad & Tobago, St. Kitts and Nevis) to control hibiscus mealybug (Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green)).
Prey / Associated habitat
HEMIPTERA: Aleyrodidae: Aleurodicus dispersus Russell. Aphididae:
Aphis punicae Passerini. Coccoidea: Birendracoccus (as Pseudococcus)
saccharifolii (Green), Coccidohystrix insolita (Green), Ferrisia virgata (Cockerell),
Icerya aegyptiaca (Douglas), Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Green), Megapulvinaria
(as Pulvinaria) maxima (Green), Nipaecoccus viridis (Newstead), Planococcus citri (Risso), Planococcus lilacinus (Cockerell), Planococcus minor (Maskell) (as P. pacificus Cox), Pseudococcus longispinus (Targioni Tozzetti), Pulvinaria (as Chloropulvinaria) polygonata Cockerell, Pulvinaria psidii Maskell, Pulvinaria
sp., Rastrococcus iceryoides (Green), Rastrococcus invadens Williams, Rastrococcus
spinosus (Robinson), Saissetia privigna De Lotto, Pinnaspis sp. ACARI: Tetranychidae: Tetranychus ludeni Zacher, Tetranychus urticae Koch. Common on mealybug and aphid infestations on brinjal, cotton, guava, mango, mulberry, teak, citrus, grapevine, Pongamia sp., Chromolaena odorata, Thevetia neriifolia, neem, etc.
Seasonal occurrence
Collected almost round the year in southern states of India.
References
- Babu, T.R. 1999. Economics of multiplication of Cryptolaemus montrouzieri Mulsant and Scymnus coccivora Aiyar, coccinellid predators. Journal of Research, ANGRAU, 27:
56-59.
- Babu, T.R. & Ramanamurthy, G. 1998. Residual toxicity of pesticides to the adults of Scymnus coccivora Aiyar (Coccinellidae: Coleoptera), a predator on mealybugs on grape. Indian Journal
of Plant Protection, 26: 96-98.
- Mani, M. & Thontadarya, T.S. 1988. Studies on the safety of different pesticides to the grape mealybug natural enemies Anagyrus dactylopii (How.) and Scymnus coccivora Ayyar.
Indian Journal of Plant Protection, 16: 205-210.
- Padmaja, C., Babu, T.R., Reddy, D.D.R. & Sriramulu, M. 1995. Biology and predation potential of Scymnus coccivora Ayyar (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on mealybugs. Journal of Entomological Research, 19: 79-81.
- Puttarudriah, M. & Channabasavanna, G.P. 1953. Beneficial coccinellids of Mysore-I. Indian Journal of Entomology, 15: 87-96.
- Puttarudriah, M. & Channabasavanna, G.P. 1956. Some beneficial coccinellids of Mysore. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 54: 156-159.
- Puttarudriah, M. & Channabasavanna, G.P. 1957. Notes on some predators of mealybugs (Coccidae, Hemiptera). The Mysore Agricultural Journal, 32: 4-19.
|