Scientific name
Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim
Taxonomic position
Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Eulophidae: Tetrastichinae
Diagnosis
Adults exhibit marked sexual dimorphism. Female 1.4-1.6 mm long, dark brown with yellow markings; head yellow except gena posteriorly brown; antenna pale brown except scape pale posteriorly; pronotum dark brown; midlobe of mesoscutum with an anterior V-shaped or inverted triangular dark brown marking, posteriorly yellow, scutellum and dorsellum light to dark brown, legs pale except fore- and hind coxae brown, fore-and mid-femora ventrally brown, pretarsi dark brown; metasoma (gaster / abdomen) brown
to dark brown, anteriorly slightly paler. Antenna with one large anellus, three funicular segments, all
longer than broad. Metasoma longer than head+mesosoma. Fore wing with one seta on submarginal vein, situated slightly basad of middle, postmarginal vein rudimentary.

 Antenna: Female (left)
and male (right) Antenna: Female (left)
and male (right)
 Fore wing venation Fore wing venation
Male smaller than female, 1.0-1.2 mm long, ground colour pale white to creamy yellow, pronotum dark brown, mesoscutum medially dark brown in anterior half, scutellum and dorsellum brown, metasoma pale in anterior half, posteriorly dark brownish, legs entirely pale. Antenna with four funicular segments, F1 much shorter than rest and transverse, other segments distinctly longer than broad, ventral plaque of scape situated in apical half.
Images


 Larvae of Q. erythrinae inside the galls Larvae of Q. erythrinae inside the galls


 Larva of Q. erythrinae Larva of Q. erythrinae


 Pupa of Q. erythrinae - ventral and dorsal view Pupa of Q. erythrinae - ventral and dorsal view




 Adult female - dorsal view Adult female - dorsal view




 Adult male - dorsal view Adult male - dorsal view

 Lateral view - male(left), and female(right) Lateral view - male(left), and female(right)

 Galls on erythrina formed by Q. erythrinae Galls on erythrina formed by Q. erythrinae

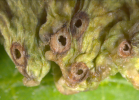
 Adult emergence holes on leaf galls Adult emergence holes on leaf galls
Distribution
The wasp is believed to be African in origin, based on the presence of closely related species. First identified in 2004 from Singapore, the Mauritius and Reunion islands; since then recorded in Taiwan, India, Thailand, Hawaii, Hong Kong, China, the Philippines, USA (Florida), Hawaii, Guam, and
American Samoa. From India, it was first recorded from Kerala (Faizal et al., 2006) and later from Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Hosts / Biology
The erythrina gall wasp forms galls on the leaves, stems, petioles, and young shoots of Erythrina spp. ("coral tree"), with at least five species known to be affected. In southern India, it has been reported to damage Erythrina stricta Roxb., a commonly used live standard for pepper and vanilla in plantations. As galls are formed on the newly emerging leaves, there is severe reduction in the number and size of leaves besides complete cessation of growth. Inside the leaf galls there is usually only one wasp per cell, whereas in the swollen tissues of shoots, twigs and petioles, more than five individuals are present (Kim et al., 2004). Affected trees appear to be scrawny with
malformed and crinkled shoots, suffer severe defoliation and ultimately die (Faizal et al., 2006).
References
- Faizal, M.H., Prathapan, K.D., Anith, K.N., Mary, C.A., Lekha, M. & Rini, C.R. 2006. Erythrina gall wasp Quadrastichus erythrinae, yet another invasive pest new to India. Current Science, 90(8): 1061-1062.
- Kim, I.K., Delvare, G. and LaSalle, J. 2004. A new species of Quadrastichus (Hymenoptera:
Eulophidae): a gall-inducing pest on Erythrina (Fabaceae). Journal of Hymenoptera Research,
13: 243-249.
|