Scientific name
Leptocybe invasa Fisher & La Salle
Common name
Eucalyptus gall wasp, Blue gum gall wasp
Taxonomic position
Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Eulophidae: Tetrastichinae
Diagnosis
Female: Color dark brown with metallic greenish / bluish tinge. Wings hyaline or lightly and uniformly infuscate. Antennal formula 11433 (anelli four-segmented). Mesoscutum without a median line. Scutellum with prominent submedian carinae. Dorsellum prominent, as long as propodeum. Fore wing with two setae on submarginal vein; postmarginal vein very short, only about a quarter as long as stigmal vein. Male: Similar to female in general appearance and coloration; antennal formula 11343 with scape having a narrow and elongate sensory organ on lateral margin, annelli three-segmented, funicle four-segmented with long latero-terminal bristles and less stout than in female, club three-segmented; abdomen somewhat tubular. Doganlar (2005) described the males as follows: head and mesosoma brown with distinct blue to green metallic shine, metasoma brown with a slightly metallic tinge, legs pale yellow, except mid and hind coxae which have metallic shine, and antennae yellow. Males are fewer and not commonly observed as the wasp is mainly thelytokous. Doganlar (2005) provided a description of the male.
 Head Head

 Mesosoma, dorsal and lateral view Mesosoma, dorsal and lateral view

 Female antenna Female antenna
 Male antenna Male antenna
 Wing venation Wing venation

 Adult female (left) and male (right) in profile Adult female (left) and male (right) in profile
Images
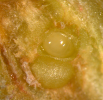
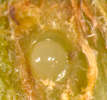
 Larva inside gall Larva inside gall
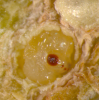

 Pupa inside gall Pupa inside gall


 Freshly emerged adult Freshly emerged adult


 Adult female Adult female




 Adult female - dorsal view Adult female - dorsal view


 Adult male - dorsal and lateral views Adult male - dorsal and lateral views
Distribution
Middle East, the Mediterranean, Europe, Africa (Mendel et al., 2004); L. invasa is thought to originate from Australia, but its situation in this country is unknown. Presently recorded from Algeria, France (including Corsica), Israel, Italy, Jordan, Morocco, Portugal, Spain, Turkey, Algeria, Jordan, Kenya, Morocco, Syria, Tanzania, Uganda, Iran, Israel, Thailand, Turkey, Vietnam, and India (known so far from Andhra Pradesh; Delhi; Karnataka; Kerala; Uttar Pradesh; Tamil
Nadu).
Hosts / Biology / Symptoms of damage
L. invasa attacks many Eucalyptus species ( E. botryoides, E. bridgesiana, E. camaldulensis, E. globulus, E. gunii, E. grandis, E. saligna, E. maidenii, E. robusta, E. tereticornis, E. viminalis). The wasp causes typical bump-shaped galls on the leaf midribs, petioles, and stems of new growth of several Eucalyptus spp., particularly in young plantations and nurseries. Larvae form galls on the leaves and tender shoots of Eucalyptus spp. Heavy galling prevents further development of the infested growth. Mendel et al. (2004) described in detail the stages of gall formation and the biology of the wasp. The wasp reproduces by thelytoky and only females have been known so far. Eggs are inserted in the epidermis of the upper side of newly developed leaves on both sides of the midrib, petiole and parenchyma tissue of twigs, always in a lined group. The section of the leaf midrib carrying the eggs turn from green to pink 1-2 weeks after oviposition. The galls are spherical and glossy green initially and later turn from green to light or dark red depending on whether the galls are on leaves or the stem. The emergence holes are light brown on the leaves and reddish brown on the stem (Mendel et al., 2004).

 Galls on seedlings Galls on seedlings
 Eucalyptus leaf with oviposition injury Eucalyptus leaf with oviposition injury
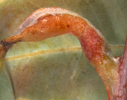

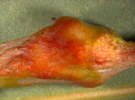

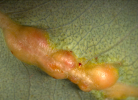
 Galls on midribs of leaves Galls on midribs of leaves

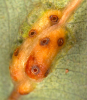
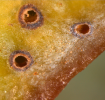 Adult emergence holes on galls Adult emergence holes on galls
References
- Doganlar, O. 2005. Occurrence of Leptocybe invasa Fisher & La Salle, 2004 (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) on Eucalyptus camaldulensis in Turkey, with a description of the male sex. Zoology in the Middle East, 35: 112-114.
- Mendel, Z., Protasov, A., Fisher, N. & La Salle, J. 2004. Taxonomy and biology of Leptocybe invasa gen. & sp. n. (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an invasive gall inducer on Eucalyptus.
Australian Journal of Entomology, 43: 101-113.
- Protasov, A., La Salle, J., Blumberg, D., Brand, D., Saphir, N., Assael, F., Fisher, N. & Mendel, Z. 2007. Biology, revised taxonomy, and impact on host plants of Ophelimus maskelli, an invasive gall inducer on Eucalyptus spp. in the Mediterranean area. Phytoparasitica, 35(1): 50-76.
|