Scientific name
Coelophora bissellata Mulsant (=Spilocaria bissellata (Mulsant), Lemnia bissellata (Mulsant))
Taxonomic position
Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Coccinellinae: Coccinellini
Diagnosis
Length 4.56-4.98 mm, width 3.95-4.25 mm. Form round, strongly convex. Head and pronotum creamy yellow or pale pink, posterior half of head with a black marking reaching up to eyes (Fig. 1). Ground colour of elytra carmine red to orange yellow on disk and margins yellowish brown. Pronotum with two pairs of black spots on posterior margin, outer pair smaller, located on posterolateral corners and inner pair much larger, subtriangular to oval, situated in middle. Each elytron with four spots
arranged in a 1-1-1-1 pattern and two common sutural spots, one in each half. Pronotal and / or elytral spots sometimes reduced in size and / or number rarely lateral borders of elytra narrowly black. Ventral side with mouthparts and legs yellowish brown, meso- and metasternal epimera white, middle of prosternum,
meso- and metasterna and middle of abdominal segments black and elytral epipleura yellowish brown. Antennae (Fig. 2) eleven-segmented, terminal segment elongate oval. Prosternal intercoxal process (Fig. 3) with a pair of carinae, anterior margin of mesosternum triangularly emarginate (Fig. 3). Abdominal postcoxal line incomplete (Fig. 4). Male genitalia (Figs. 7-9), female genital plate (Fig. 5) and spermatheca (Fig. 6) as illustrated.
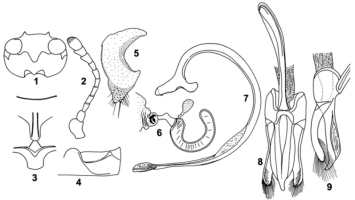 Figs. 1-9. Coelophora bissellata: 1. Head; 2. Antenna; 3. Prosternal intercoxal process; 4. Postcoxal line on abdominal ventrite 1; 5. Female genital plate; 6. Spermatheca; 7-9. Male genitalia: 7. Sipho; 8. Tegmen, ventral view; 9. Tegmen, lateral view. Figs. 1-9. Coelophora bissellata: 1. Head; 2. Antenna; 3. Prosternal intercoxal process; 4. Postcoxal line on abdominal ventrite 1; 5. Female genital plate; 6. Spermatheca; 7-9. Male genitalia: 7. Sipho; 8. Tegmen, ventral view; 9. Tegmen, lateral view.Images




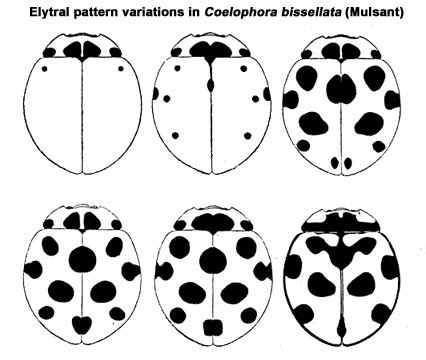 Elytral pattern variations in C. bissellata Elytral pattern variations in C. bissellata
Distribution
India: Widely distributed (Assam; Himachal Pradesh; Karnataka; Kerala; Manipur; Meghalaya; Punjab; Sikkim; Tamil Nadu; Uttar Pradesh; West Bengal). Nepal. Bangladesh. Bhutan. Thailand. China. Indonesia. The Philippines. New Guinea.
Prey / Associated habitat
HEMIPTERA: Aphidoidea: Adelges spp., Aphis craccivora Koch, Aphis
fabae Scopoli, Aphis gossypii Glover, Cervaphis rappardi indica Basu, Rhopalosiphum maidis (Fitch), Toxoptera aurantii (Boyer de Fonscolombe), Toxoptera odinae (van der Goot). ACARI: Raoiella indica Hirst on areca palm. Collected on sugarcane, rice, cowpea, Beta vulgaris, areca palm, sandal, Argemone sp., Pterolobium indicum, Webera corymbosa, and spruce.
Seasonal occurrence
Collected during January, April-May, July-August (South India), and October-December
(Eastern region).
Natural enemy
Acari: Podapolipidae: Coccipolipus sp.
References
- Kapur, A.P. 1962. Geographical variations in the colour pattterns of some Indian Ladybeetles (Coccinellidae: Coleoptera). Part I. Coccinella septempunctata Linn., C. transversalis Fabr., and Coelophora bissellata Muls. Proceedings of the First All India Congress of Zoology (1959), 2: 479-492.
- Puttarudriah, M. & Channabasavanna, G.P. 1953. Beneficial coccinellids of Mysore-I. Indian
Journal of Entomology 15: 87-96.
- Puttarudriah, M. & Channabasavanna, G.P. 1955. Beneficial coccinellids of Mysore-II. Indian
Journal of Entomology 17: 1-5.
- Rhamhalinghan, M. 1989. Studies on Coelophora bissellata Muls. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). 1. Field recognition of different larval instars and the traits of pupae and adults. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 86: 114-117.
|