Classification
Aphidinae: Macrosiphini
Common name(s)
Safflower aphid
Diagnosis
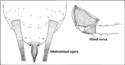
Medium-sized to large (1.9-4.1 mm), broadly spindle-shaped, very dark red to almost black aphids with black siphunculi and cauda, colonizing flower stems and in lower numbers along the midribs of the leaves of Compositae. The aphids are shiny but relatively less in numbers than U. sonchi. Antenna as long as body, segment three equal to or little longer than segment IV and V put together. Siphunculi double or little less in length of that of cauda. Cauda as dark as siphunculi. Cauda with 16-17 hairs.
The aphid makes dense colonies near flower stalks and also damage young shoots. If not controlled, the aphid can cause serious damage leading to death of the plant.
Distribution
Widely distributed in Africa and the Indian subcontinent (India: Karnataka); Mauritius, Taiwan, South America, Sicily.
Host plant(s)
Asteraceae: Carthamus tinctorius L.
Measurements
Aptera: Length of body 3.76, width 1.71; antennae 3.73, segments III: IV: V: VI 1.12: 0.60: 0.51: (0.16+1.05); u.r.s. 0.18; h.t.2 0.15; siphunculus 1.19; cauda 0.60.
Alata: Length of body 2.85, width 0.97; antennae 3.11, segments III: IV: V: VI 0.92: 0.51: 0.48: (0.16+0.99); u.r.s. 0.16; h.t.2 0.15; siphunculus 0.80; cauda 0.40.
Seasonal occurrence
November-March.
Natural enemies
Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Brumoides suturalis (F.), Cheilomenes sexmaculata (F.).
Diptera: Syrphidae: Ischiodon scutellaris (F.), Paragus yerburiensis Stuckenberg, Sphaerophoria ?indiana Bigot.