Classification
Aphididae: Drepanosiphinae
Common name(s)
Crapemyrtle aphid
Diagnosis
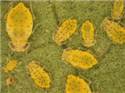
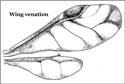
Apterae and alates distinctive, 1.6-1.8 mm, pale to bright yellow, with dark sclerotic rows of pigmented tubercles bearing capitate hairs. Alatae also have rows of pigmented tubercles on dorsal side of abdomen, those on tergite 2 medially fused with the process to form a dark sclerotic transverse band. Antennae 0.53 times as long as body. Processus terminalis as long as base of the last antennal segment. Ultimate rostral segment almost equal to ht2. Abdomen (Fig. 1) with paired spinal processi on anterior tergites with well developed lateral tubercles bearing one hair each. Siphunculi pale, small and smooth. Cauda rounded in apterae and knobbed in alatae. Wing venation (Fig. 2) normal, wings strongly pigmented, dark over stigmal and costal areas and at base. Tips of veins pigmented.
Distribution
India (Assam, West Bengal, Kerala, Karnataka), China, Taiwan, Japan, Hawaii, the USA.
Host plant(s)
Lythraceae: Lagerstroemia indica L.
Measurements
Aptera: Length of body 1.62, width 0.85; antennae 0.86, segments III: IV: V: VI 0.28: 0.28: 0.09: (0.09+0.09); u.r.s. 0.060; h.t.2 0.068; cauda 0.07.
Alata: Length of body 1.65, width 0.79; antennae 1.13, segments III: IV: V: VI 0.33: 0.22: 0.21: (0.09+0.10); u.r.s. 0.07; h.t.2 0.07; siphunculi 0.03; cauda 0.09.
Seasonal occurrence
October-December.
Natural enemies
Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Cheilomenes sexmaculata (F.).